Thyroid cancer, a diagnosis that strikes fear into the hearts of many, is often met with uncertainty and apprehension. The word “cancer” alone can evoke images of a relentless, life-threatening adversary. But is thyroid cancer fatal as it sounds? In this blog, we embark on a journey to explore its various facets and provide insight into the prognosis and treatment options available.
What is thyroid cancer?
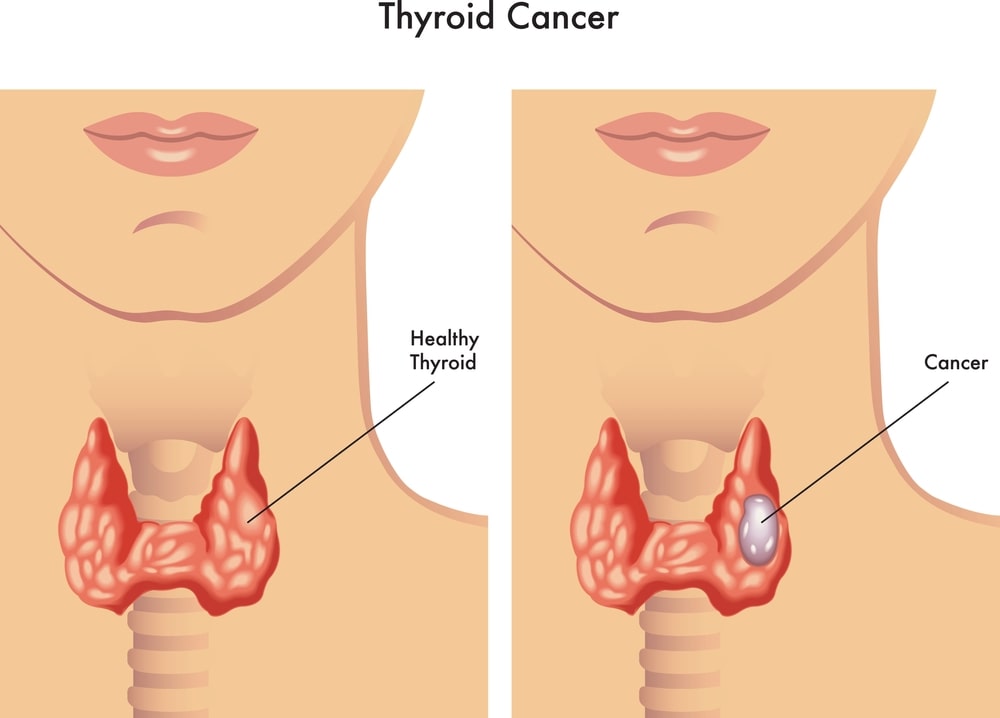
Thyroid cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the thyroid gland, which is a butterfly-shaped organ located in the front of the neck, just below the Adam’s apple. The thyroid gland is responsible for producing hormones that regulate various bodily functions, including metabolism. Read on to know if Is Thyroid Cancer Fatal.
There are several different types of thyroid cancer, with the most common ones being:
- Papillary thyroid cancer: This is the most common type of thyroid cancer and tends to grow slowly. It often affects people in their 30s and 40s.
- Medullary thyroid cancer: Medullary thyroid cancer originates from the C cells in the thyroid gland, which produce calcitonin. It is less common than papillary and follicular thyroid cancers.
- Follicular thyroid cancer: This type is less common than papillary thyroid cancer and also tends to grow slowly. It typically affects older individuals.
- Hurthle cell carcinoma: This type of thyroid cancer is a variant of follicular thyroid cancer and is characterized by the presence of Hurthle cells.
- Anaplastic thyroid cancer: This is a rare and aggressive form of thyroid cancer that can spread quickly. It is often diagnosed in older individuals.
Thyroid cancer may not always present with noticeable symptoms in its early stages, and it is often discovered during a routine physical examination or imaging tests for other medical conditions. Let’s find out “Is thyroid cancer fatal” later in the blog.
What causes thyroid cancer?
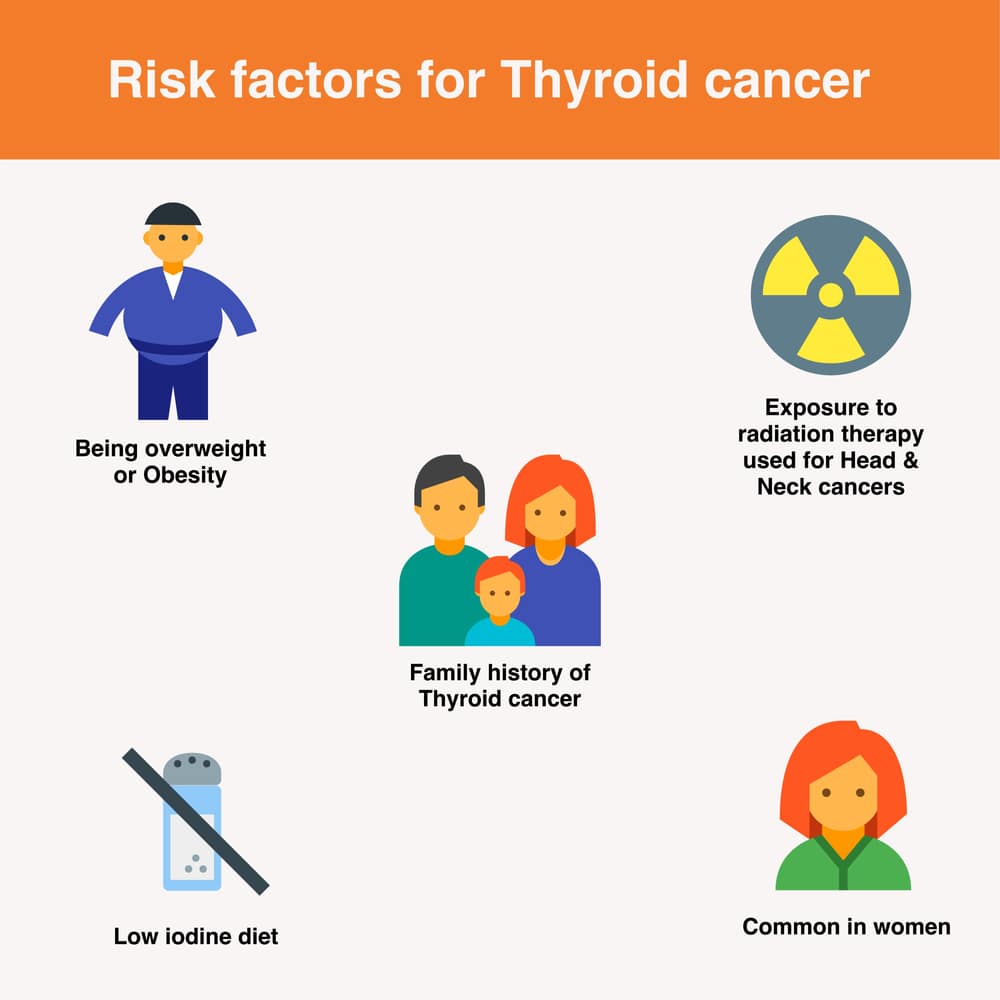
- Genetic Factors: Some genetic mutations and familial syndromes are associated with an increased risk of thyroid cancer.
- Gender and Age: Thyroid cancer is more common in women than in men, and the risk of developing thyroid cancer tends to increase with age. It is most often diagnosed in people between the ages of 30 and 60.
- Radiation Exposure: Exposure to ionizing radiation, especially during childhood or adolescence, is a well-established risk factor for thyroid cancer.
- Family History: Having a family history of thyroid cancer may slightly elevate an individual’s risk, particularly for certain genetic forms of the disease.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain environmental toxins and pollutants, although less well-established, has also been studied as a potential risk factor for thyroid cancer.
- Diet and Lifestyle: Some studies have suggested a potential connection between a high intake of goitrogenic foods (which can interfere with thyroid function) and thyroid cancer risk, but more research is needed to confirm these associations. Scroll down to learn about is thyroid cancer fatal.
What are the symptoms of thyroid cancer?

Common symptoms of thyroid cancer may include:
- Difficulty Swallowing: Thyroid nodules or tumors can sometimes grow to a size that causes difficulty in swallowing or a feeling of a “lump in the throat.”
- Changes in Voice: may manifest as hoarseness or voice changes.
- Neck Lump or Enlarged Thyroid Gland: One of the most common signs of thyroid cancer is the presence of a painless lump or nodule in the neck.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck may be palpable or visible.
- Neck Pain: Some individuals with thyroid cancer may experience pain in the neck, which can radiate to the ears.
- Thyroid Dysfunction Symptoms: include weight changes, fatigue, changes in heart rate, mood swings, and changes in appetite. Keep on reading if you want to know is thyroid cancer fatal.
How is thyroid cancer treated?

The primary treatment modalities for thyroid cancer may include:
- Surgery: Surgery is the most common and often the initial treatment for thyroid cancer. The extent of surgery can vary:
- Thyroidectomy: This is the removal of all or part of the thyroid gland. The type of thyroidectomy performed depends on the size and extent of the tumor. If only one lobe of the thyroid is removed, it’s called a lobectomy, whereas removing the entire thyroid is known as a total thyroidectomy.
- Lymph Node Dissection: In some cases, nearby lymph nodes may also be removed if they are involved or suspected to be involved with cancer.
- Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy: After a total thyroidectomy, patients will need to take synthetic thyroid hormones (Levothyroxine) for life. This replaces the hormone production that the thyroid gland would typically provide and helps maintain normal thyroid hormone levels in the body.
- Targeted Therapy and Chemotherapy: Targeted therapies aim to block specific molecules that promote cancer growth, while chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Lenvatinib, Cabozantinib, and Sorafenib are targeted drugs called multikinase inhibitors, as they work by inhibiting several different kinase proteins. These medications act in two major ways: They help block tumors from forming new blood vessels, which the tumors need to grow.
- External Beam Radiation Therapy: This treatment is less common for thyroid cancer and is typically reserved for certain cases, such as when cancer has spread to nearby structures or when it is not responding to other treatments. This blog gives you a clear understanding of what is thyroid cancer and is thyroid cancer fatal.
Is Thyroid Cancer Fatal?
Thyroid cancer, in general, has a relatively favorable prognosis, and many people with thyroid cancer have a good chance of long-term survival. The outcome largely depends on several factors, including the type of thyroid cancer, the stage at diagnosis, the age and overall health of the individual, and the effectiveness of treatment.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer: Anaplastic thyroid cancer is a rare and highly aggressive form of thyroid cancer. It has a poorer prognosis and is often associated with lower survival rates. Treatment for anaplastic thyroid cancer can be challenging.
- Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Medullary thyroid cancer has a somewhat lower survival rate compared to papillary and follicular thyroid cancer. The prognosis can vary, especially depending on whether it is sporadic or hereditary. Genetic testing and early diagnosis are important in managing this type of thyroid cancer.
- Papillary and Follicular Thyroid Cancer: These are the most common types of thyroid cancer and tend to be associated with a very high survival rate, especially when detected early. The 10-year survival rate for these types is often greater than 90%.
- Favorable Prognostic Factors: Favorable prognostic factors for thyroid cancer include early detection, small tumor size, well-differentiated cancer cells, and a younger age at diagnosis.
- Treatment Effectiveness: The effectiveness of treatment plays a significant role in the outcome. Surgery is often the primary treatment, followed by radioactive iodine therapy, targeted therapy, or external beam radiation in certain cases. The response to these treatments can vary among individuals.
- Recurrence: Thyroid cancer can recur, even many years after initial treatment. Regular follow-up and monitoring are crucial to detect and manage any recurrences or complications.
FAQs:
Is thyroid cancer curable?
Thyroid cancer is often curable, especially when detected early and treated appropriately. The curability depends on factors like the type and stage of cancer, treatment effectiveness, and individual patient characteristics. Most individuals with thyroid cancer have a good chance of long-term survival, but outcomes can vary, and regular monitoring is essential to detect any recurrences or complications.
Is thyroid cancer hereditary?
Thyroid cancer can have both hereditary and non-hereditary causes. While the majority of cases are not directly linked to genetics, some forms of thyroid cancer, such as medullary thyroid cancer (MTC), can have a hereditary component.
Can thyroid cancer spread?
Yes, thyroid cancer can spread to other parts of the body, a process known as metastasis. The likelihood and pattern of metastasis depend on several factors, including the type of thyroid cancer, its stage at the time of diagnosis, and the effectiveness of treatment. Common sites for metastasis in thyroid cancer may include nearby lymph nodes, as well as distant organs such as the lungs, bones, and other tissues.
How do you get thyroid cancer?
Thyroid cancer can develop due to a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. While the exact cause is not always clear, risk factors may include exposure to radiation, certain genetic syndromes, family history of thyroid cancer, and, in some cases, iodine deficiency or excess. Most cases of thyroid cancer are not directly linked to modifiable behaviors, and the disease often arises spontaneously.
What is the most common treatment for thyroid cancer?
The most common treatment for thyroid cancer is surgery, which typically involves removing all or part of the thyroid gland. This procedure is known as a thyroidectomy. The extent of surgery depends on the type and stage of the cancer. So, by now you might have a better understanding of is thyroid cancer fatal.