Joint pain can be a debilitating condition that affects people of all ages and backgrounds. Whether it stems from aging, injury, or an underlying medical condition, joint pain can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Fortunately, there are various joint pain treatment options available to alleviate pain and restore mobility.
Typical locations for common joint pain to appear are the hands, feet, hips, knees, or spine. Pain may come and go or be constant. On occasion, the joint may feel stiff, achy, or sore. Some patients describe a burning, throbbing, or “grating” sensation. Additionally, the joint may be stiff in the morning but get looser and feel better as you move around.
Excessive exercise, though, can make the pain worse. Simple tasks can become challenging for someone with joint discomfort, and it may even affect how effectively the joint functions. Extreme joint discomfort may influence the quality of life.
Treatment should concentrate on the impaired activities and functioning as well as the discomfort. In this blog, we will explore a range of approaches, from lifestyle modifications to medical interventions, to help you find effective relief and regain control over your joint health.
Understanding the Causes: What Causes Joint Pain?

Before delving into treatment options, it is essential to identify the root cause of your joint pain. Common causes include arthritis (osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis), joint injuries, bursitis, tendinitis, gout, and lupus.
- Osteoarthritis, a frequent form of arthritis, emerges over time as the cartilage, which acts as a cushion between the bones, deteriorates. The joints begin to ache and stiffen. Osteoarthritis typically develops in middle age and advances gradually.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic illness that damages the joints and causes swelling. The fingers and wrists are the most commonly affected by joint abnormalities.
- In the severe disorder known as gout, body crystals accumulate in the joint, causing excruciating pain and swelling. typically happens in the big toe.
- Bursitis is caused by overuse. It typically manifests as pain in the shoulder, elbow, hip, or knee.
- Joint mobility may be uncomfortable due to viral infections, rash, or fever.
- Injuries such as sprains or shattered bones.
- The flexible bands that connect bone and muscle are called tendons, and tendinitis is an inflammation of them. It is frequently brought on by overuse and typically manifests in the elbow, heel, or shoulder.
Consulting with a healthcare professional, such as a rheumatologist or orthopedic specialist, will help you determine the specific cause of your joint pain and devise an appropriate treatment plan.
Joint Pain Treatments:
Even while there may not be a cure for the pain, it can be managed to give the sufferer some relief. Sometimes the discomfort can be relieved with over-the-counter medication or a straightforward daily workout regimen.
Sometimes, though, discomfort may indicate a condition that needs to be treated with medication or surgery.
Joint Pain Treatments also include Lifestyle Modifications which can include Diet and Natural Remedies for Joint Pain Management listed below:
Balanced Diet:

Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet can help manage joint pain. Supplements for the diet, such as glucosamine, may help with pain management. Consult a doctor before using any over-the-counter supplements.
Furthermore, include foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (salmon, walnuts), antioxidants (berries, leafy greens), and spices with anti-inflammatory properties (turmeric, ginger). Making certain dietary changes can support joint health and alleviate pain. Consider the following:
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), flaxseeds, and chia seeds. Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce joint pain.
Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Consume a variety of fruits and vegetables rich in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and colorful vegetables. Antioxidants help combat inflammation and promote overall health.
Healthy Fats: Include sources of healthy fats in your diet, such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil. Healthy fats can provide lubrication to the joints and reduce inflammation.
Let’s just understand: Avoid processed foods, excessive sugar, and saturated fats, as they may contribute to inflammation.
Exercise and Weight Management:

Regular exercise is crucial for maintaining joint health. Low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, and walking can strengthen muscles around the joints, provide support, and improve flexibility. Weight management is also important, as excess weight puts additional strain on joints.
Weight loss, if necessary, can lessen the strain on joints. Maintaining a healthy body weight can help reduce joint pain and prevent further damage.
Exercise can help you regain strength and function. Low-impact aerobic exercise, like walking or swimming, is ideal. People who participate in strenuous workouts or sports may need to scale back their involvement or begin low-impact exercise programs.
Body-stretching exercises will be advantageous. Consult your doctor before beginning or continuing any fitness program.
Rest and Joint Care:

Balance periods of activity with adequate rest.
Avoid overusing or straining your joints, and consider using supportive devices like braces or splints.
Implementing proper ergonomics at home and work, along with modifying repetitive tasks, can reduce stress on joints.
Exercise can keep your joints strong and reduce fatigue and stiffness. Meanwhile, getting a good night’s sleep can help you better manage pain and fatigue.
Physical Therapy and Exercise:
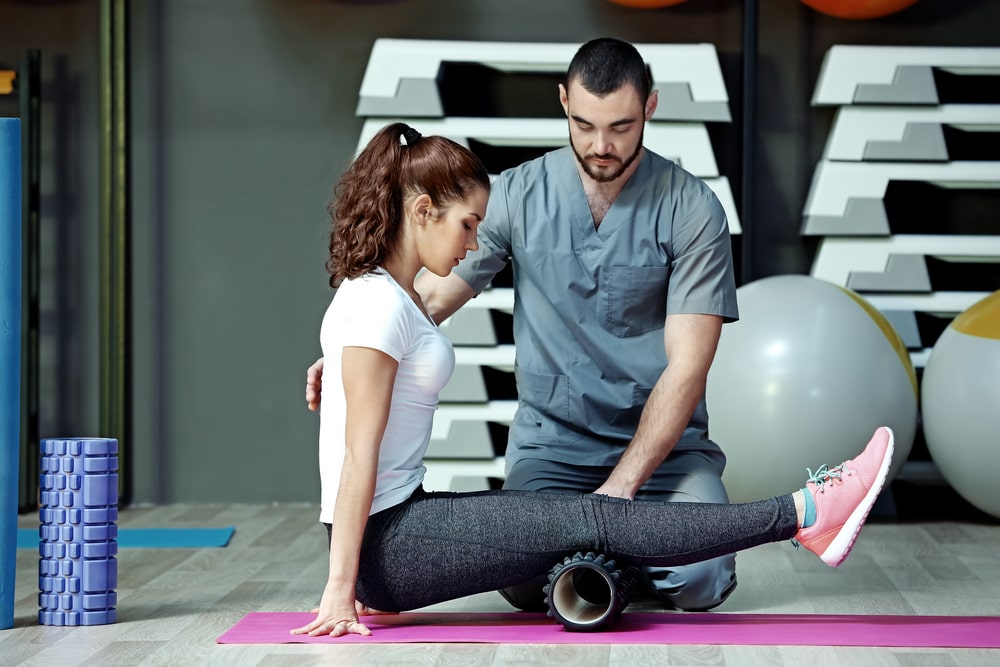

Physical therapy plays a vital role in joint pain treatment. A physical therapist can guide you through tailored exercises and stretches that improve joint mobility, strengthen supporting muscles, and reduce pain.
Examples of aerobic exercises that are easy on joints include walking, bicycling, swimming and water aerobics. Try to work up to 150 minutes of somewhat hard aerobic exercise every week.
They may also employ techniques like heat or cold therapy, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation to alleviate discomfort.
Alternative Therapies:
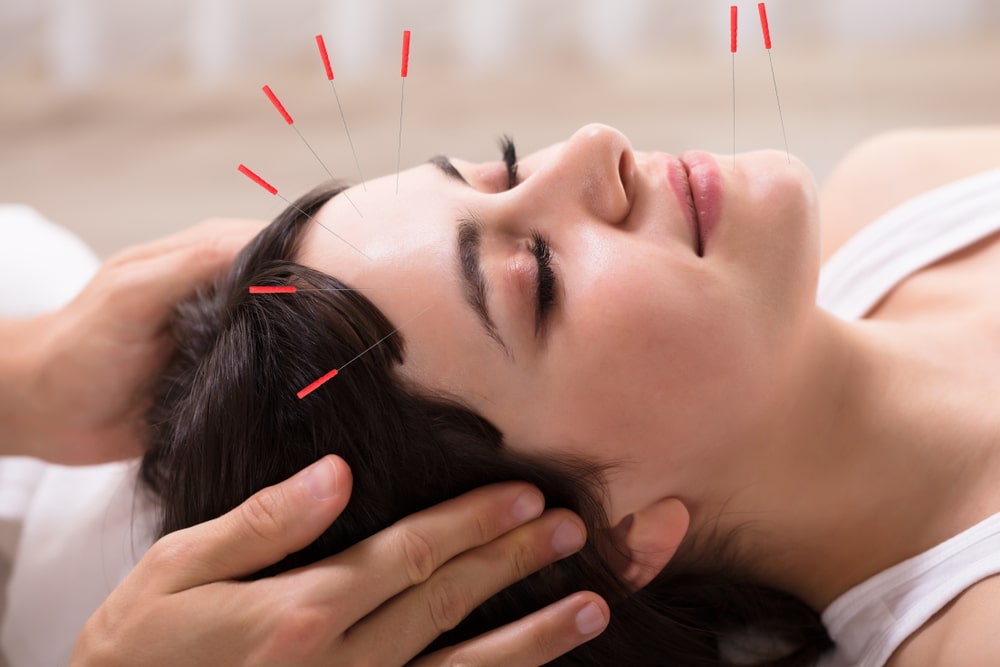

Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese therapy involves inserting fine needles into specific body points to promote pain relief and restore balance. Acupuncture has shown promising results in managing joint pain and improving joint function.
Massage Therapy: This therapy can help relax muscles, relieve tension, and improve blood flow to affected joints. It may provide temporary relief from joint pain and contribute to overall well-being.
It may be advised to use a heating pad or an ice pack on the affected area for brief intervals several times each day as one of the straightforward at-home treatments. Warm-water baths may also be soothing.
Topical Treatments:
It is easy to feel overwhelmed by the number of topical creams, balms, gels, patches, and sprays available to treat joint pain.
Knowing about these products’ active ingredients and relative effectiveness can help people select the ones best suited for them.
They can ease discomfort including ointments or gels that can be massaged into the skin over the painful joint area.
Some of them can be bought over the counter or without a prescription, respectively.
Topical anesthetics such as lidocaine produce a numb sensation to reduce pain. Lidocaine is available in the form of a cream, gel, spray or patch.
Surgical Interventions:
In cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical options may be considered.
Procedures such as joint replacement, arthroscopy, or joint fusion can be effective in reducing pain and restoring joint function.
These interventions are typically recommended for severe arthritis or joint damage.
Natural Remedies for Joint Pain Management: Finding Relief the Natural Way
Joint pain can be a persistent and uncomfortable condition, affecting individuals of all ages. While there are conventional treatments available, many people prefer to explore natural remedies for managing joint pain due to concerns about side effects or a desire for a more holistic approach.
Exercise and Physical Activity:
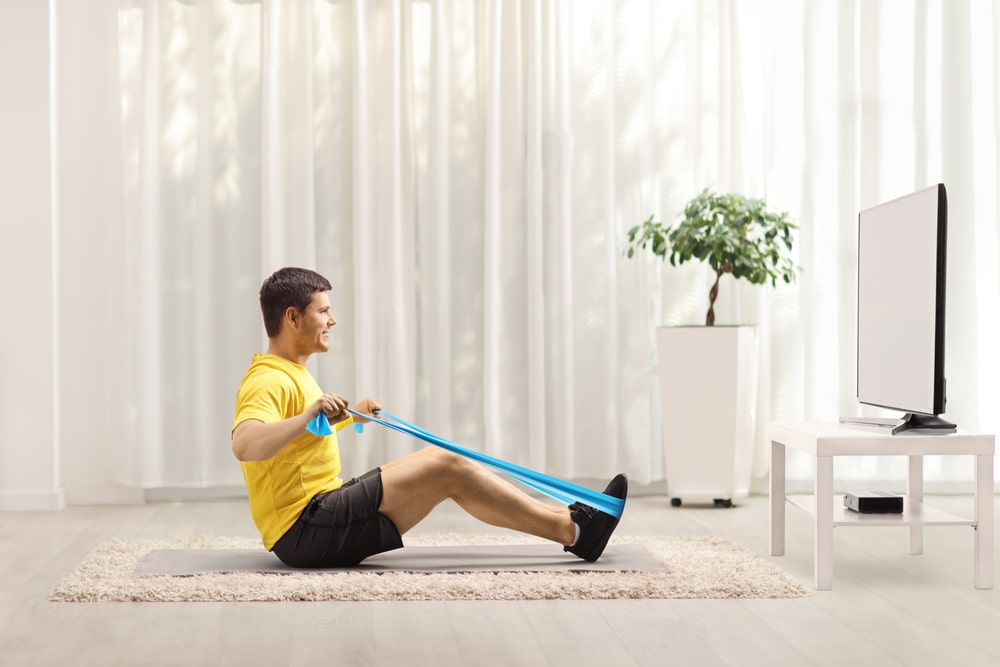

Engaging in regular exercise and physical activity is one of the most effective natural remedies for joint pain.
Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, and yoga help strengthen the muscles around the joints, improve flexibility, and reduce stiffness.
Exercise also promotes the production of endorphins, natural pain-relieving chemicals in the body.
Counsel for low-impact physical activities—Walking, biking, swimming, and water activities are all good non-drug ways to ease joint pain.
These are safe for most adults. These forms of exercise can also improve joint function and improve mood.
Hot and Cold Therapy:
Applying hot or cold packs to the affected joints can provide temporary relief from joint pain.
Heat therapy, such as warm baths or heating pads, helps relax muscles and increase blood flow to the joints.
Cold therapy, using ice packs or cold compresses, can reduce inflammation and numb the area, thereby alleviating pain.
Alternate between hot and cold treatments for maximum benefit. Heat helps loosen tight muscles and joints and relieves pain and muscle spasms.
If you have swelling, it’s best to use ice for 24 hours, then switch to heat. If swelling isn’t a problem, it’s fine to use heat when you first notice joint pain.
Herbal Supplements:
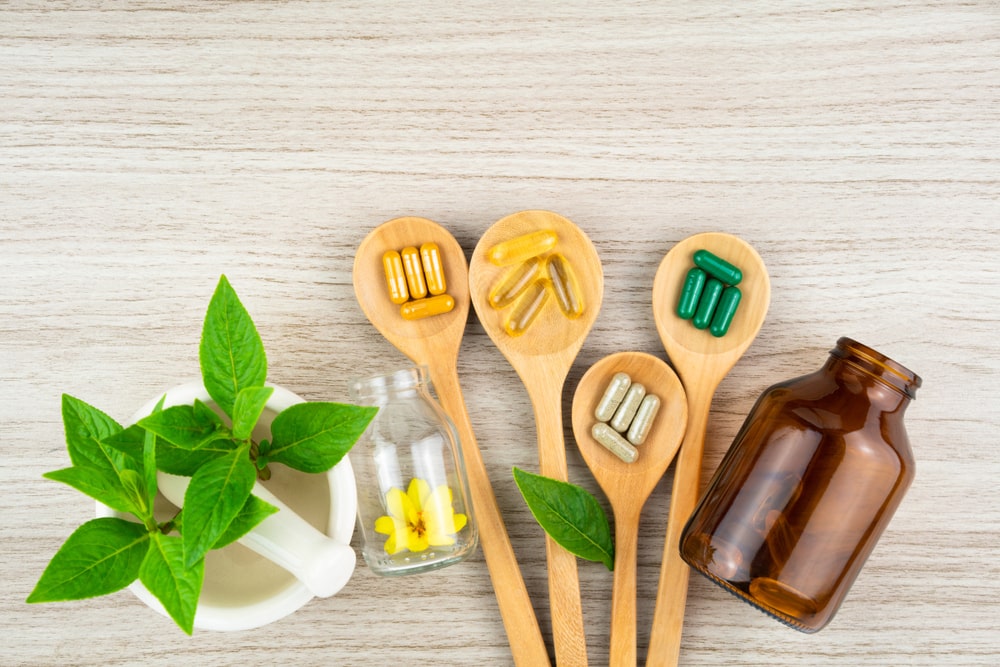

Certain herbal supplements have gained popularity for their potential benefits in managing joint pain. These include:
a) Turmeric: Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, has strong anti-inflammatory properties. Taking turmeric supplements or incorporating turmeric into your diet may help reduce joint pain and inflammation.
b) Ginger: Ginger contains gingerols, which possess anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. Consuming ginger tea or adding ginger to your meals can provide relief from joint pain.
c) Boswellia: Also known as Indian frankincense, boswellia extract has been traditionally used to manage joint pain and inflammation. It may help improve joint mobility and reduce swelling.
d) Devil’s Claw: Derived from the root of the devil’s claw plant, this herb has been used for centuries to alleviate joint pain and stiffness.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating herbal supplements into your routine, as they may interact with medications or have contraindications for certain health conditions.
Essential Oils:
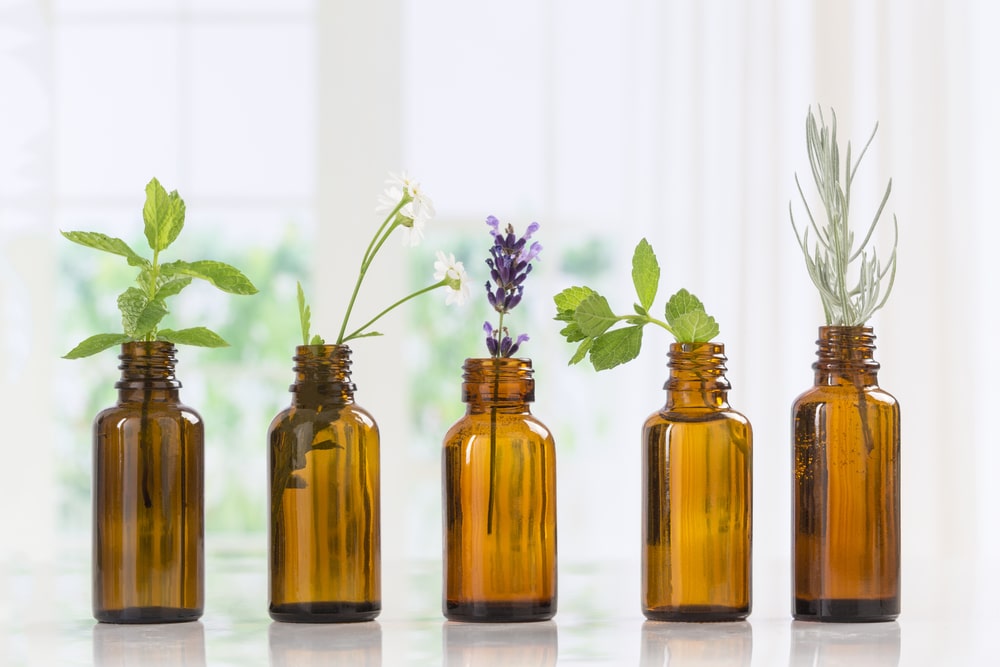

Several essential oils have analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties that can aid in joint pain management. Popular options include:
a) Eucalyptus Oil: Known for its cooling effect, eucalyptus oil can help reduce pain and inflammation. Dilute it with carrier oil and massage it onto the affected joints.
b) Peppermint Oil: Peppermint oil provides a soothing sensation and can relieve muscle and joint pain. Mix it with carrier oil and gently massage it onto the affected area.
c) Lavender Oil: Lavender oil has calming and anti-inflammatory properties. Applying diluted lavender oil topically may help reduce joint pain and promote relaxation.
Mind-Body Techniques:
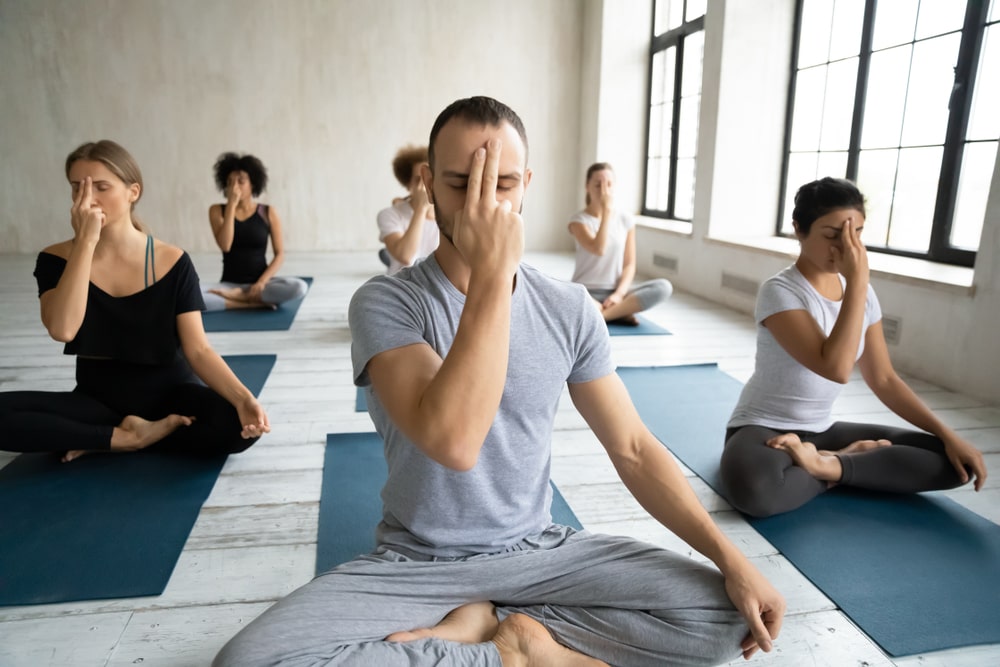

The connection between our mind and body is a powerful one. Our brains control all our bodily processes, including chronic pain!
This doesn’t mean that your pain is “all in your head” or not real. All pain is created by our brains, even acute pain.
Managing stress and incorporating mind-body techniques can positively impact joint pain.
Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help reduce stress levels, improve relaxation, and potentially alleviate joint pain.
Joint Pain Medications:
They play a significant role in managing pain, reducing inflammation, and improving joint function. It’s important to note that the choice of medication depends on the underlying cause of joint pain and should be determined by a healthcare professional. Here are some commonly prescribed medications for joint pain:
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs):
NSAIDs are widely used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation associated with joint conditions like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Common examples include Ibuprofen, Naproxen Sodium, and Diclofenac. While NSAIDs are available over-the-counter, stronger prescription-strength NSAIDs may be recommended for more severe joint pain. Eg: Aspirin, Diclofenac.
Acetaminophen:
Acetaminophen, commonly known as Tylenol, is an analgesic that can help relieve pain, but it has little to no anti-inflammatory effects. It is often recommended for individuals who cannot tolerate NSAIDs or have conditions that may interact with NSAIDs. Eg: Paracetamol.
Corticosteroids:
Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, can be administered orally, injected into the joint, or applied topically as a cream or gel. They are powerful anti-inflammatory medications that help reduce pain and inflammation in the joints. Corticosteroid injections are often used for localized joint pain and are particularly effective for conditions like bursitis or tendinitis. Eg: Prednisone, Methylprednisolone.
Disease-Modifying Anti-rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs):
DMARDs are commonly prescribed for rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune forms of arthritis. They modify the underlying disease process, reduce inflammation, and slow down joint damage. Examples of DMARDs include Methotrexate, Sulfasalazine, and Hydroxychloroquine.
Biologic Response Modifiers:
Biologic response modifiers, also known as biologics, are a type of DMARD that targets specific proteins involved in the immune system’s inflammatory response. These medications are typically administered through injection or infusion and are reserved for moderate to severe cases of conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. Examples of biologics include Adalimumab, Etanercept, and Infliximab.
Opioids:
In cases of severe and chronic joint pain that is unresponsive to other treatments, opioids may be prescribed. Opioids are strong pain relievers that work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain, reducing the perception of pain. However, due to their potential for dependence and side effects, opioids are generally used cautiously and for short periods under close medical supervision. Eg: Demerol, Oxycontin.
Over-the-Counter Pain Medications:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and naproxen sodium can help reduce joint pain and inflammation. However, long-term use should be supervised by a healthcare professional to minimize potential side effects. Eg: Ibuprofen.
It’s crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and instructions provided by your healthcare professional when using joint pain medications. They will consider factors such as the severity of pain, the underlying condition, and potential interactions with other medications or health conditions. Regular communication with your healthcare provider is important to monitor the effectiveness and adjust the treatment plan if needed.
End Note:
Living with joint pain can be challenging, but there are numerous treatment options available to alleviate discomfort and enhance your quality of life. By adopting a holistic approach that combines lifestyle modifications, physical therapy, medication, and alternative therapies, you can find relief and regain control over your joint health.
Remember to consult with healthcare professionals to determine the most suitable treatment plan for your specific condition. With proper care and persistence, you can overcome joint pain and enjoy a life of comfort and mobility.
FAQs:
Can Ozempic cause joint pain?
No, it does not cause joint pain.
Can stress cause joint pain?
Yes, if the body is under stress, it releases certain chemicals that can cause pain and inflammation in the body.
Is joint pain a symptom of Covid?
Yes, Joint pain is a major symptom of Covid, experienced by a maximum number of patients.
Can low iron cause joint and muscle pain?
Yes, Low iron can be a reason for these kinds of pains.
Can dehydration cause joint pain?
Dehydration can cause muscle spasms in the body and in turn, can lead to joint pain.
Can gluten cause joint pain?
Yes, gluten can lead to joint pain for those who are sensitive to a gluten diet.
Can statins cause joint pain?
Yes, statins can cause joint pain.
Does CBD help with joint pain?
In preclinical trials, the non-psychoactive Cannabidiol (CBD) showed promise in reducing arthritis-related pain and can be effective in joint pain treatment.


